From Qiime2 into R - Initial diagnostics
Packages
library(qiime2R)
library(tidyverse)
library(stringr)
library(vegan)
library(phyloseq)
Import qiime files
## use this vector to set factor levels (this is only needed if you want treatments
## in a certain order for your figures)
### 'levelsvector' is added to steps below.
levelsvector = c("Control", "H2O2","Heat", "Inositol", "SodiumFormate", "SodiumAcetate",
"CitricAcid", "FumaricAcid", "Lime", "PoultryLitter", "Biochar")
## metadata
# This is the same metadata file that was used in qiime2
metadata<- readr::read_tsv("metadata.tsv")
metadata2 <- metadata[c(2:nrow(metadata)),c(1:length(metadata))] %>%
tibble::rownames_to_column("spl") %>%
dplyr::mutate_all(type.convert) %>%
dplyr::mutate_if(is.factor, as.character) %>%
tibble::column_to_rownames("spl")
# rename, add or edit factors
metadata2$Treatment[metadata2$Treatment == "AutoclavedControl"] <- "Heat"
metadata2$Treatment <- factor(metadata2$Treatment, levels=levelsvector)
metadata2$Week <- factor(metadata2$Week, levels=c("T0","T39","T52","Reference", "Blank"))
metadata2 <- metadata2 %>% as_tibble() %>% column_to_rownames("#SampleID")
## Import of Qiime2 feature table (ASV abundances)
SVs <- qiime2R::read_qza("feature_table_insertiontreefiltered.qza")
## Import taxonomy file
## I found it easier to use a tsv file. I.e. after creating the qiime taxonomy.qzv I
## opened the file visualisation in https://view.qiime2.org/ and downloaded the .tsv from there.
taxonomy <- read_tsv("taxonomy_silva.tsv") %>%
filter(Taxon != "categorical") %>%
rename(Feature.ID = `Feature ID`)
## re-format the taxonomy file to split the taxonomy into columns
## remove the confidence column
taxtable <- taxonomy %>% as_tibble() %>%
separate(Taxon, sep=";", c("Kingdom","Phylum","Class","Order","Family","Genus","Species")) %>%
dplyr::select(-Confidence) %>%
column_to_rownames("Feature.ID") %>%
as.matrix()
## Import qiime tree file, here the insertion-tree.qza, see https://library.qiime2.org/plugins/q2-fragment-insertion/16/
tree <- read_qza("insertion-tree-silva.qza")
Create a phyloseq object
## combine all to a phyloseq object
physeqB <- phyloseq::phyloseq(
phyloseq::otu_table(SVs$data, taxa_are_rows = T),
phyloseq::phy_tree(tree$data),
phyloseq::tax_table(taxtable),
phyloseq::sample_data(metadata2) )
## Remove those annoying short codes in front of taxa names (i.e. p__ etc) as they
## dont look good in visualisation
tax_table(physeqB)[, "Kingdom"] <- str_replace_all(tax_table(physeqB)[, "Kingdom"], "d__", "")
tax_table(physeqB)[, "Phylum"] <- str_replace_all(tax_table(physeqB)[, "Phylum"], " p__", "")
tax_table(physeqB)[, "Class"] <- str_replace_all(tax_table(physeqB)[, "Class"], " c__", "")
tax_table(physeqB)[, "Order"] <- str_replace_all(tax_table(physeqB)[, "Order"], " o__", "")
tax_table(physeqB)[, "Family"] <- str_replace_all(tax_table(physeqB)[, "Family"], " f__", "")
tax_table(physeqB)[, "Genus"] <- str_replace_all(tax_table(physeqB)[, "Genus"], " g__", "")
tax_table(physeqB)[, "Species"] <- str_replace_all(tax_table(physeqB)[, "Species"], " s__", "")
physeqB
## phyloseq-class experiment-level object
## otu_table() OTU Table: [ 22271 taxa and 136 samples ]
## sample_data() Sample Data: [ 136 samples by 6 sample variables ]
## tax_table() Taxonomy Table: [ 22271 taxa by 7 taxonomic ranks ]
## phy_tree() Phylogenetic Tree: [ 22271 tips and 22189 internal nodes ]
Initial filtering
Filter out any ASVs that have less than 10 reads and are present in less than 3 samples. Then filter out any phyla that came up as uncharacterized and taxa that came up as mitochondria and chloroplast.
# filter as needed. This will be your final otu-table.
# Although you can still filter for specific analysis if needed.
# minimum of reads per feature
physeqB.flt = prune_taxa(taxa_sums(physeqB) >= 10, physeqB) #minimum reads per feature
physeqB.flt = filter_taxa(physeqB.flt, function(x) sum(x > 0) > (0.015*length(x)), TRUE) #minimum presense in x% of samples (136 * 0.015 = 2 samples)
#filter any phyla that have not been classified i.e. are "NA"
physeqB.flt = subset_taxa(physeqB.flt, !is.na(Phylum) & !Phylum %in% c("", "uncharacterized"))
# Filter out non-bacteria, mitochondia and chloroplast taxa
physeqB.flt <- physeqB.flt %>%
subset_taxa(Kingdom == "Bacteria" & Family != "Mitochondria" & Class != "Chloroplast"
& !is.na(Phylum) & !Phylum %in% c("", "uncharacterized") )
physeqB.flt
## phyloseq-class experiment-level object
## otu_table() OTU Table: [ 4932 taxa and 136 samples ]
## sample_data() Sample Data: [ 136 samples by 6 sample variables ]
## tax_table() Taxonomy Table: [ 4932 taxa by 7 taxonomic ranks ]
## phy_tree() Phylogenetic Tree: [ 4932 tips and 4931 internal nodes ]
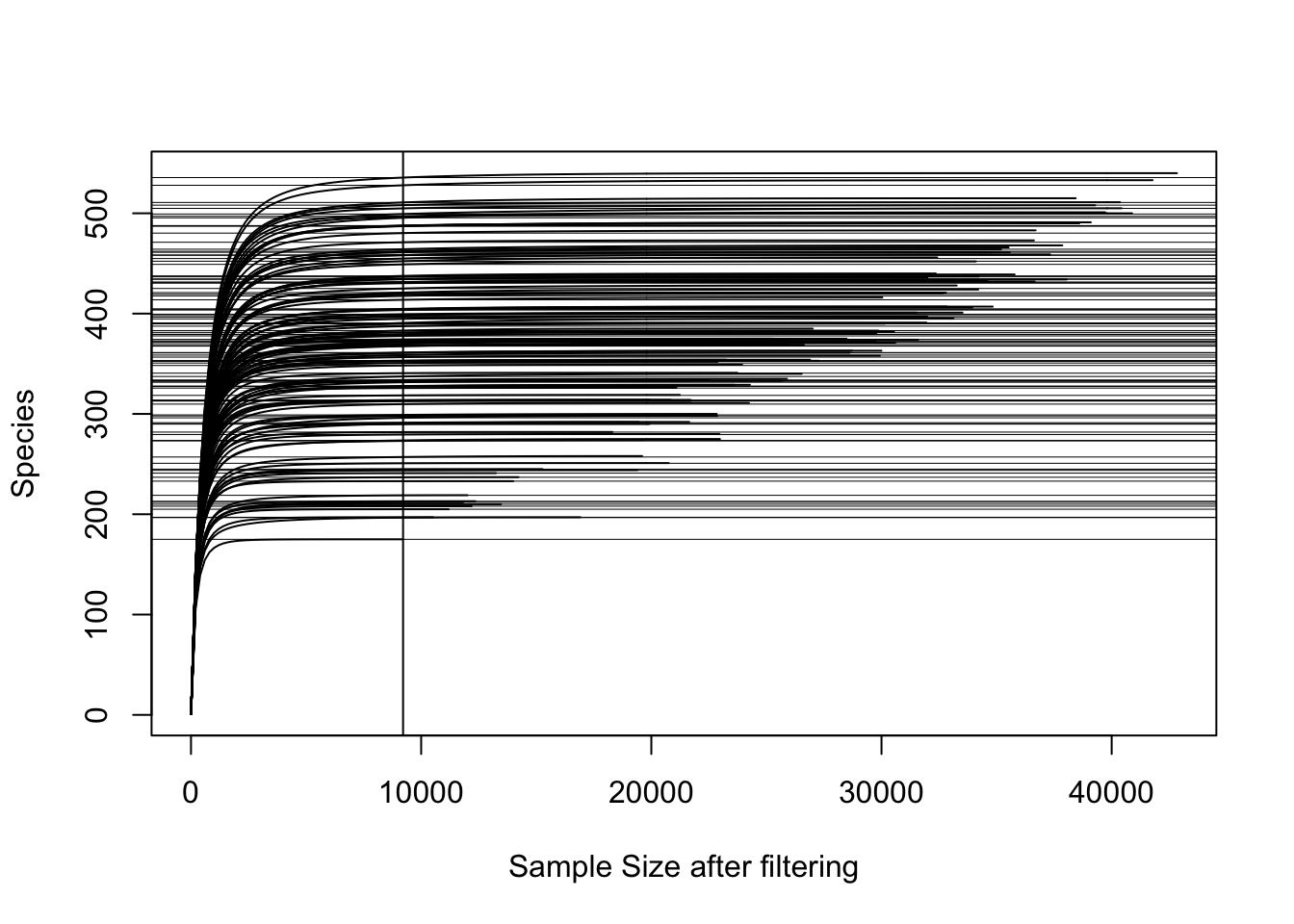
Rarefaction curve
Check if you cover enough depth for diversity analyses. In this case I had to remove references, blanks, autoclaved soils and soils treated with hydrogen peroxide before doing diversity analyses.
#filter
`%notin%` = Negate(`%in%`)
#physeqB.flt.norefs <- prune_samples(sample_data(physeqB.flt)$Name %notin% c("41AutoclavedControlT0","42AutoclavedControlT0","43AutoclavedControlT0","44AutoclavedControlT0"), physeqB.flt)
physeqB.flt.norefs <- prune_samples(sample_data(physeqB.flt)$Treatment %notin% c("Heat", "H2O2"), physeqB.flt)
physeqB.flt.norefs <- prune_samples(sample_data(physeqB.flt.norefs)$Treatment != "Reference", physeqB.flt.norefs)
physeqB.flt.norefs <- prune_samples(sample_data(physeqB.flt.norefs)$Treatment != "Blank", physeqB.flt.norefs)
physeqB.flt.norefs <- phyloseq::prune_taxa(taxa_sums(physeqB.flt.norefs) != 0, physeqB.flt.norefs)
vegan::rarecurve(t(otu_table(physeqB.flt.norefs)), step=200, sample = min(colSums(otu_table(physeqB.flt.norefs))), label = FALSE, xlab = "Sample Size after filtering")
Prevelance table
Create a prevalence table to see which phyla have low prevalence
## Create a prevalence table to see which phyla have low prevalence
physeqB.flt.prevtab <- prune_samples(sample_data(physeqB.flt)$Treatment != "Reference", physeqB.flt)
physeqB.flt.prevtab <- prune_samples(sample_data(physeqB.flt.prevtab)$Treatment != "Blank", physeqB.flt.prevtab)
prevelancedf = apply(X = phyloseq::otu_table(physeqB.flt.prevtab),
MARGIN = 1,
FUN = function(x){sum(x > 0)})
prevelancedf = data.frame(Prevalence = prevelancedf,
TotalAbundance = taxa_sums(physeqB.flt.prevtab),
phyloseq::tax_table(physeqB.flt.prevtab))
prevelancedf <- plyr::ddply(prevelancedf, "Phylum", function(df1){
data.frame(mean_prevalence=mean(df1$Prevalence), total_abundance=sum(df1$TotalAbundance,na.rm = T), stringsAsFactors = F)
})
prevelancedf
## Phylum mean_prevalence total_abundance
## 1 Acidobacteriota 7.214912 199741
## 2 Actinobacteriota 8.756279 708045
## 3 Armatimonadota 4.954545 2062
## 4 Bacteroidota 5.981818 20919
## 5 Bdellovibrionota 3.000000 30
## 6 Chloroflexi 9.567042 646439
## 7 Cyanobacteria 3.333333 135
## 8 Dependentiae 3.333333 72
## 9 Desulfobacterota 4.875000 1572
## 10 Firmicutes 14.844250 1101043
## 11 Gemmatimonadota 5.800000 17851
## 12 Myxococcota 5.909091 27926
## 13 Nitrospirota 4.235294 2300
## 14 Planctomycetota 6.509174 177762
## 15 Proteobacteria 8.713961 557906
## 16 RCP2-54 6.666667 3067
## 17 Verrucomicrobiota 8.205128 54178
## 18 WPS-2 5.870968 20024
Note:
This code is an amalgamation from various sources. Apart from putting it together into a pipeline I do not take credit for it.